Your cart is currently empty!

Python High-Order Functions: A Comprehensive Guide
Python High-Order Functions
As we delve deeper into Python programming, we encounter fascinating concepts that enhance code flexibility and efficiency. One such powerful concept is High-Order Functions. In this tutorial, we’ll explore high-order functions, their properties, and how to implement them in Python effectively.
Table of Contents
Download New Real Time Projects :-Click here

Prerequisites
Before diving into high-order functions, ensure you are familiar with the following:
- Python functions
- Parameters in Python
- Python objects
- Python decorators
What are High-Order Functions?
A high-order function is one that either:
- Accepts another function as an argument.
- Returns a function as its output.
High-order functions are very versatile since they work on other functions. These could be functions or methods that return functions as results or accept functions as parameters.
Properties of High-Order Functions in Python
High-order functions in Python have several noteworthy properties:
- Function as a Variable: Variables can be given functions.
- Function as an Object: Functions can behave like objects.
- Returning Functions: Another function may be returned by a function.
- Functions as Parameters: It is possible to provide functions as parameters to other functions.
- Storage in Data Structures: High-order functions can be stored in data structures like lists or dictionaries.
Defining High-Order Functions in Python
We can implement high-order functions in several ways. Below are some key approaches:
- Using functions as objects
- Passing functions as parameters
- Returning functions as results
- Using decorators
Let’s discuss each method with examples.
1. Using Functions as Objects
In Python, functions are first-class citizens, meaning they can be assigned to variables, stored, and passed around.
Example:
# Function to convert text to uppercase
def spell(text):
return text.upper()
# Assigning function to a variable
scream = spell
# User input
text = input("Enter a text to convert to uppercase: ")
# Invoking the first function
print(spell(text))
# Calling the function via the assigned variable
print(scream(text))
Output:
Enter a text to convert to uppercase: Python
PYTHON
PYTHON
2. Functions as Parameters
Since Python functions are objects, they can be passed as arguments to other functions, creating high-order functions.
Example:
# Function to convert text to uppercase
def scream(word):
return word.upper()
# Function to convert text to lowercase
def whisper(word):
return word.lower()
# High-order function accepting another function
def speak(func):
message = func("Welcome to the world of Python!")
print(message)
# Calling with different functions
speak(scream)
speak(whisper)
Output:
WELCOME TO THE WORLD OF PYTHON!
welcome to the world of python!
3. Returning Functions
Other functions can be the output of high-order functions. This approach is particularly useful for creating nested or dynamic functions.
Example:
# Function returning another function
def adder(a):
def addition(b):
return a + b
return addition
# User input
x = int(input("Enter the first number: "))
y = int(input("Enter the second number: "))
# Getting the returned function
add = adder(x)
# Using the returned function
result = add(y)
print(f"The sum of {x} and {y} is {result}.")
Output:
Enter the first number: 10
Enter the second number: 20
The sum of 10 and 20 is 30.
4. Decorators as High-Order Functions
Decorators are a popular use case of high-order functions. They modify or extend the behavior of functions without permanently changing them.
Example:
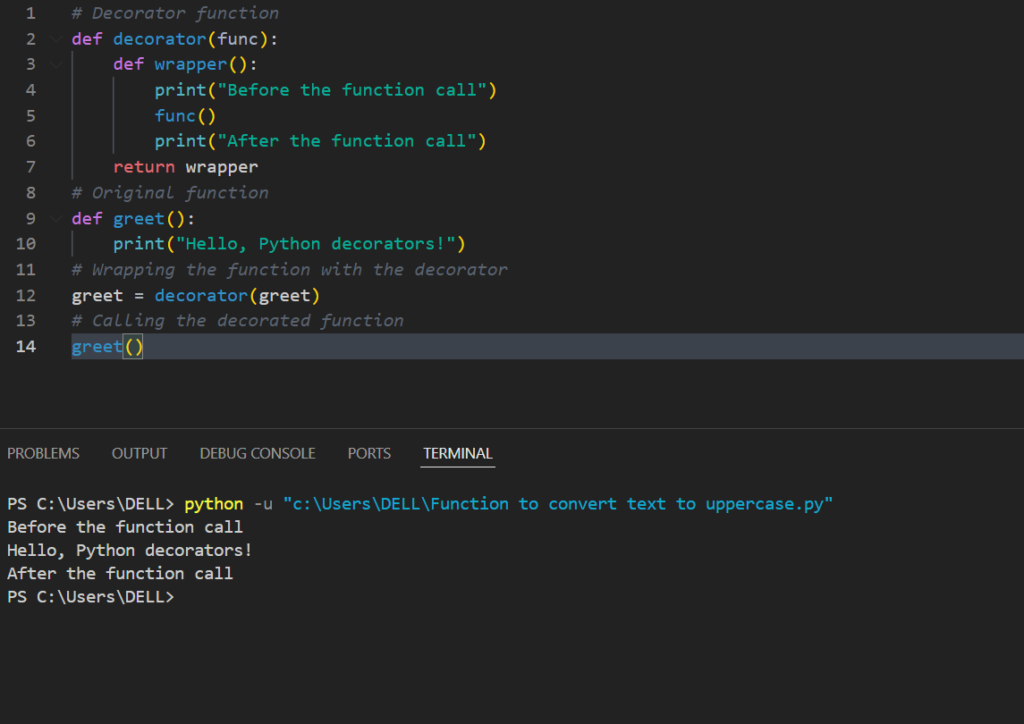
# Decorator function
def decorator(func):
def wrapper():
print("Before the function call")
func()
print("After the function call")
return wrapper
# Original function
def greet():
print("Hello, Python decorators!")
# Wrapping the function with the decorator
greet = decorator(greet)
# Calling the decorated function
greet()
Output:
Before the function call
Hello, Python decorators!
After the function call
PHP PROJECT:- CLICK HERE
INTERVIEW QUESTION:-CLICK HERE
Complete Advance AI topics:- CLICK HERE
Complete Python Course with Advance topics:- CLICK HERE
- higher-order functions python examples
- Python High-Order Functions
- higher order functions python w3schools
- python higher order functions list
- python higher-order functions type hint
- lambda function in python
- Python High-Order Functions
- python functools
- higher-order functions python lambda
- python lru_cache
- python high-order functions
- python higher order functions with parameters
- python higher order functions type hint
- python higher order functions exercises
- Python High-Order Functions
Leave a Reply