Third Normal Form (3NF)
Third Normal Form (3NF)
Third Normal Form (3NF) is a crucial step in relational database design that guarantees minimal redundancy and data integrity. If a relation has no transitive dependencies and is already in Second Normal Form (2NF), it is said to be in 3NF. This form is essential for maintaining data consistency and cutting down on repetition.
Let’s explore what 3NF entails, how to achieve it, and why it matters.
Machine Learning Tutorial:–Click Here
Data Science Tutorial:-Click Here
Complete Advance AI topics:- CLICK HERE
Deep Learning Tutorial:- Click Here
What is Third Normal Form (3NF)?
A relation is in Third Normal Form if for every non-trivial functional dependency X → Y, at least one of the following conditions holds:
- X is a super key, or
- Y is a prime attribute—that is, an attribute that is part of some candidate key.
To put it simply, a non-prime attribute should not be transitively dependent on the primary key. When these rules are followed, we eliminate unnecessary redundancy and make the structure more robust.
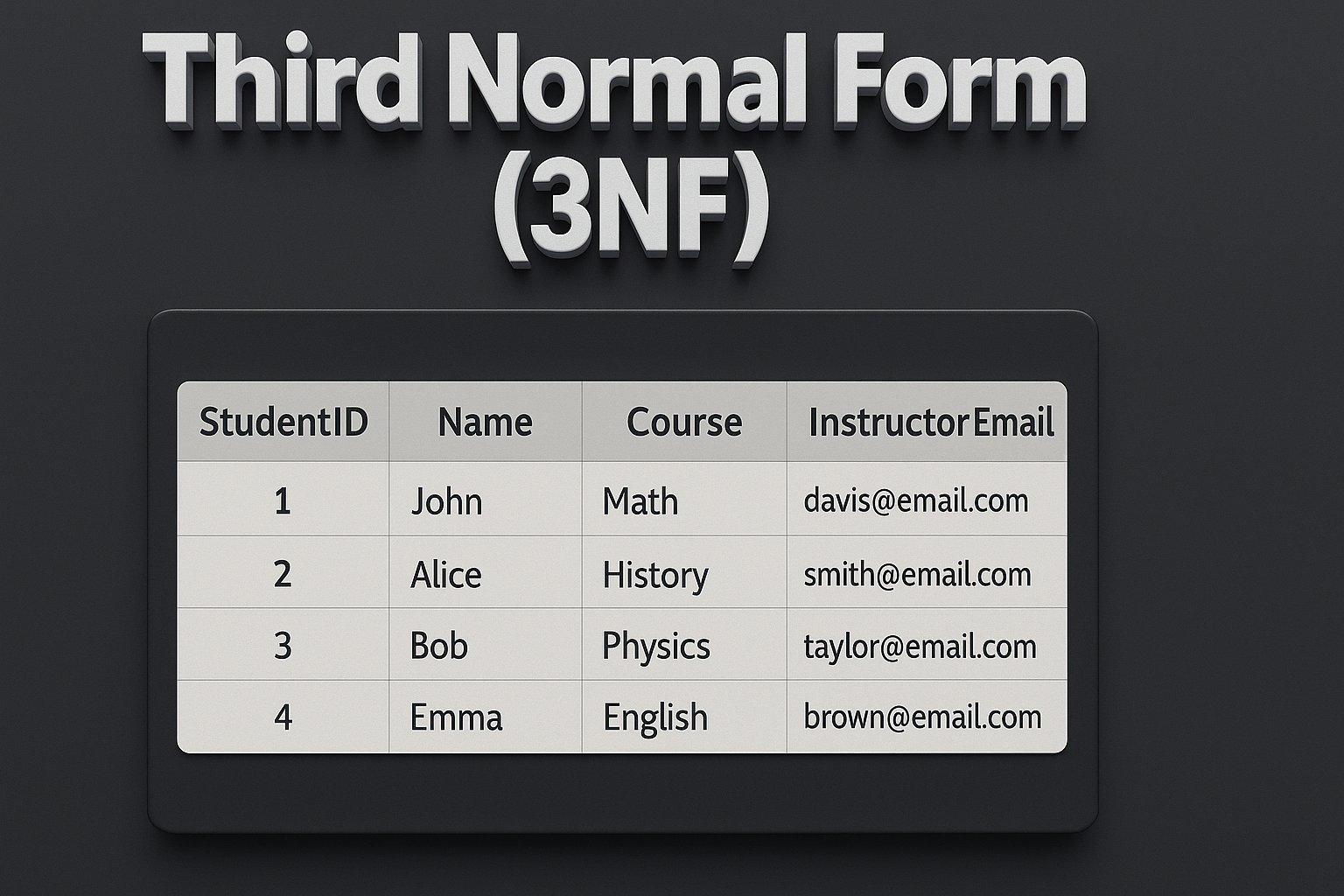
Example: EMPLOYEE_DETAIL Table
Consider the following table:
| EMP_ID | EMP_NAME | EMP_ZIP | EMP_STATE | EMP_CITY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 222 | Harry | 201010 | UP | Noida |
| 333 | Stephan | 02228 | US | Boston |
| 444 | Lan | 60007 | US | Chicago |
| 555 | Katharine | 06389 | UK | Norwich |
| 666 | John | 462007 | MP | Bhopal |
- Candidate Key:
{EMP_ID} - Super Keys:
{EMP_ID},{EMP_ID, EMP_NAME},{EMP_ID, EMP_NAME, EMP_ZIP}, etc. - Non-prime Attributes: All except EMP_ID.
In this table, notice that EMP_STATE and EMP_CITY depend on EMP_ZIP, which in turn depends on EMP_ID. This transitive dependency violates the rules of 3NF, even though the table may be in 2NF.
Achieving 3NF
We divided the table into two sections in order to remove transitive dependencies:
EMPLOYEE Table:
| EMP_ID | EMP_NAME | EMP_ZIP |
|---|---|---|
| 222 | Harry | 201010 |
| 333 | Stephan | 02228 |
| 444 | Lan | 60007 |
| 555 | Katharine | 06389 |
| 666 | John | 462007 |
EMPLOYEE_ZIP Table:
| EMP_ZIP | EMP_STATE | EMP_CITY |
|---|---|---|
| 201010 | UP | Noida |
| 02228 | US | Boston |
| 60007 | US | Chicago |
| 06389 | UK | Norwich |
| 462007 | MP | Bhopal |
There are no transitive dependencies left with this structure; all non-key attributes are directly dependent on the primary key. This satisfies 3NF and reduces redundancy.
Anomalies in 3NF
Even after achieving 3NF, certain anomalies might still occur—insertion, deletion, and update anomalies, especially when multivalued dependencies exist.
Let’s consider another example using the STAFF relation.
STAFF Relation
Initially, it’s represented as:
STAFF (@S_Name + @Equipment + @Language)
Here, @ indicates the primary key.
After converting it to 1NF for proper relational structure:
| S_Name | Equipment | Language |
|---|---|---|
| Anurag | PC | English |
| Anurag | PC | French |
| Anurag | Mainframe | English |
| Anurag | Mainframe | French |
| Kapil | PC | English |
| Kapil | PC | French |
| Kapil | PC | Japanese |
In this format:
- A combination of S_Name, Equipment, and Language makes up the primary key.
- There are no transitive dependencies, hence the relation is in 3NF.
- However, it still faces anomalies:
Insertion Anomaly:
If Anurag learns Japanese, new rows must be added for each equipment he uses. This causes unnecessary repetition.
Deletion Anomaly:
If Anurag’s PC is deallocated, deleting all entries related to that equipment may also remove information about languages he knows—resulting in data loss.
Update Anomaly:
Changing a staff name (e.g., from Anurag to Anuraj) requires multiple updates, increasing the risk of inconsistency.
These anomalies are the result of multivalued dependencies, not addressed by 3NF. The solution lies in progressing to the Fourth Normal Form (4NF), which we will cover in a future post.
Complete Python Course with Advance topics:-Click Here
SQL Tutorial :-Click Here
Download New Real Time Projects :-Click here
Conclusion
A crucial stage in database normalisation is the Third Normal Form. It reduces redundancy and improves data integrity by eliminating transitive dependencies. However, it doesn’t eliminate all forms of anomalies—especially those arising from multivalued dependencies. Understanding the limitations of 3NF helps database designers prepare for more advanced normalization, such as 4NF.
For deeper normalization strategies and advanced database design, stay tuned to Updategadh.
third normal form in dbms
third normal form in dbms with example
1st, 2nd and 3rd normal form examples
boyce-codd normal form
bcnf in dbms
third normal form example answers
second normal form
4th normal form
third normal form 3nf in dbms
third normal form 3nf example
third normal form 3nf pdf








Post Comment