Understanding Join Operations in DBMS
Join Operations
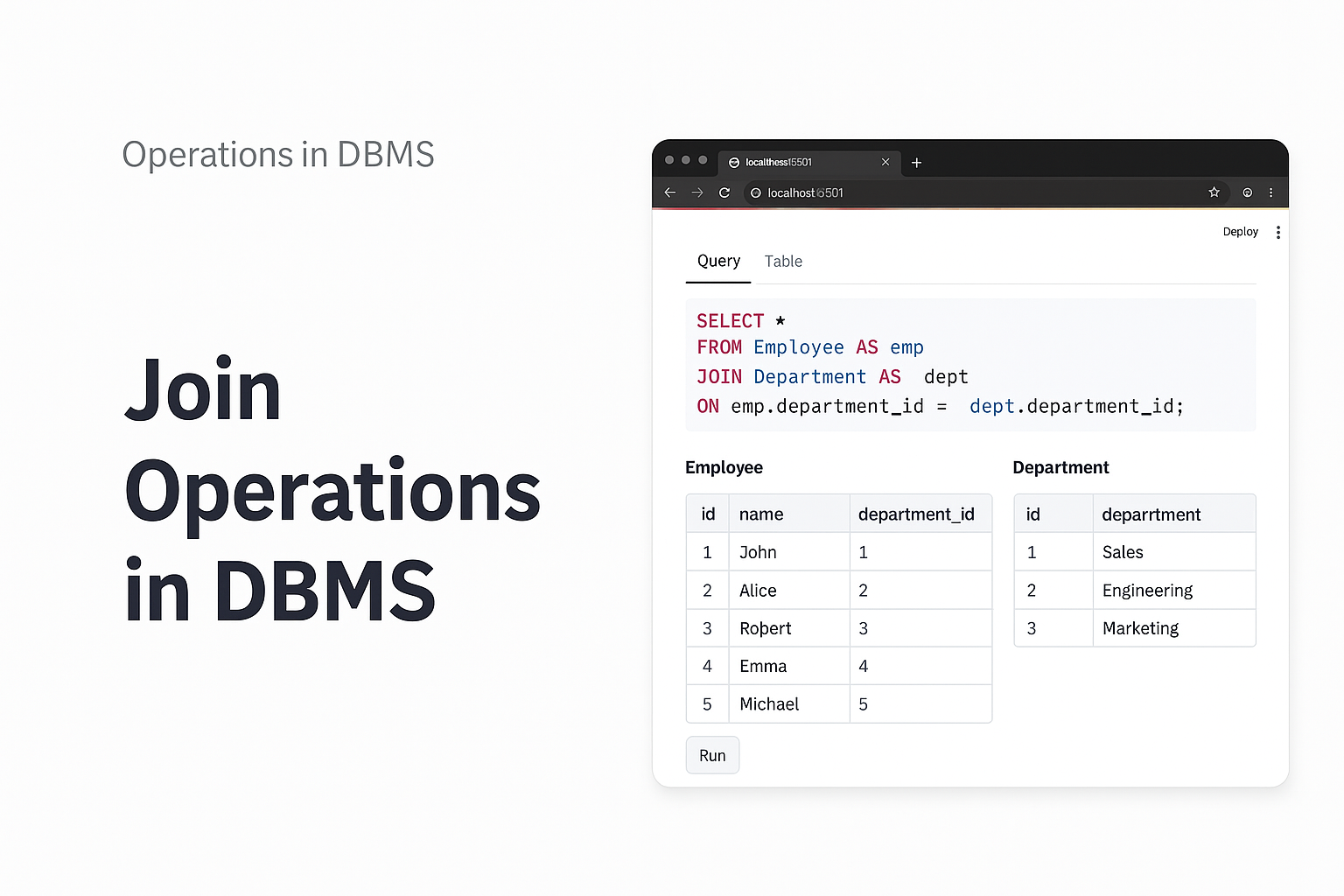
In relational database systems, the Join operation plays a pivotal role in retrieving meaningful information from multiple tables based on a specified condition. Denoted by the symbol (⋈), a join operation consolidates related tuples from two or more relations when a defined join condition is met. This article offers a comprehensive overview of the different types of join operations, supported by illustrative examples, to elucidate their significance and usage in database management.
Machine Learning Tutorial:-Click Here
Data Science Tutorial:-Click Here
Complete Advance AI topics:- CLICK HERE
Deep Learning Tutorial:- Click Here
Basic Join Example
Tables:
EMPLOYEE
| EMP_CODE | EMP_NAME |
|---|---|
| 101 | Stephan |
| 102 | Jack |
| 103 | Harry |
SALARY
| EMP_CODE | SALARY |
|---|---|
| 101 | 50000 |
| 102 | 30000 |
| 103 | 25000 |
Operation: EMPLOYEE ⋈ SALARY
Result:
| EMP_CODE | EMP_NAME | SALARY |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Stephan | 50000 |
| 102 | Jack | 30000 |
| 103 | Harry | 25000 |
Types of Join Operations
1. Natural Join
When two relations have the same name, a Natural Join automatically matches their columns and merges their values. Duplicate columns are removed from the result set.
Syntax Example:
π EMP_NAME, SALARY (EMPLOYEE ⋈ SALARY)
Result:
| EMP_NAME | SALARY |
|---|---|
| Stephan | 50000 |
| Jack | 30000 |
| Harry | 25000 |
2. Outer Join
An Outer Join extends the functionality of the standard join by including non-matching rows from one or both tables, addressing the issue of missing data.
a. Left Outer Join (⟕)
This join returns all records from the left relation (EMPLOYEE) and matched records from the right relation (FACT_WORKERS). NULL values for the right table’s columns will be present in records in the left table that do not match those in the right table.
EMPLOYEE Table:
| EMP_NAME | STREET | CITY |
|---|---|---|
| Ram | Civil line | Mumbai |
| Shyam | Park street | Kolkata |
| Ravi | M.G. Street | Delhi |
| Hari | Nehru nagar | Hyderabad |
FACT_WORKERS Table:
| EMP_NAME | BRANCH | SALARY |
|---|---|---|
| Ram | Infosys | 10000 |
| Shyam | Wipro | 20000 |
| Kuber | HCL | 30000 |
| Hari | TCS | 50000 |
Operation: EMPLOYEE ⟕ FACT_WORKERS
Result:
| EMP_NAME | STREET | CITY | BRANCH | SALARY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ram | Civil line | Mumbai | Infosys | 10000 |
| Shyam | Park street | Kolkata | Wipro | 20000 |
| Hari | Nehru nagar | Hyderabad | TCS | 50000 |
| Ravi | M.G. Street | Delhi | NULL | NULL |
b. Right Outer Join (⟖)
This join returns all records from the right relation (FACT_WORKERS) and the matched records from the left relation (EMPLOYEE). Unmatched records in the left table are replaced with NULLs.
Operation: EMPLOYEE ⟖ FACT_WORKERS
Result:
| EMP_NAME | BRANCH | SALARY | STREET | CITY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ram | Infosys | 10000 | Civil line | Mumbai |
| Shyam | Wipro | 20000 | Park street | Kolkata |
| Hari | TCS | 50000 | Nehru nagar | Hyderabad |
| Kuber | HCL | 30000 | NULL | NULL |
c. Full Outer Join (⟗)
All records from both tables are returned by this join, which inserts NULLs where no match can be found and matches them where it can.
Operation: EMPLOYEE ⟗ FACT_WORKERS
Result:
| EMP_NAME | STREET | CITY | BRANCH | SALARY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ram | Civil line | Mumbai | Infosys | 10000 |
| Shyam | Park street | Kolkata | Wipro | 20000 |
| Hari | Nehru nagar | Hyderabad | TCS | 50000 |
| Ravi | M.G. Street | Delhi | NULL | NULL |
| Kuber | NULL | NULL | HCL | 30000 |
3. Equi Join (Inner Join)
An Equi Join, commonly known as an Inner Join, retrieves only those records where the specified equality condition is satisfied.
CUSTOMER Relation:
| CLASS_ID | NAME |
|---|---|
| 1 | John |
| 2 | Harry |
| 3 | Jackson |
PRODUCT Relation:
| PRODUCT_ID | CITY |
|---|---|
| 1 | Delhi |
| 2 | Mumbai |
| 3 | Noida |
Operation: CUSTOMER ⋈ PRODUCT
Result:
| CLASS_ID | NAME | PRODUCT_ID | CITY |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | 1 | Delhi |
| 2 | Harry | 2 | Mumbai |
| 3 | Jackson | 3 | Noida |
Complete Python Course with Advance topics:-Click Here
SQL Tutorial :-Click Here
Download New Real Time Projects :-Click here
Conclusion
Join operations are essential in relational database systems for merging data across multiple tables based on specific conditions. From simple natural joins to complex outer joins, each type serves a distinct purpose in ensuring data integrity and completeness. A thorough understanding of these join types empowers database professionals to write efficient queries and manage relational data structures effectively.
For more database-related tutorials and insights, stay connected with Updategadh.
join operations in dbms
joins in sql with examples
sql join
inner join
cross join
left join
cross join in sql
full outer join
join operations in sql
join operations example
join operations w3schools
types of join operations
join operations in sql server join operations in dbms
different types of join operations in dbms
sql join operations in dbms
algorithms for selection sorting and join operations in dbms
algorithms for select and join operations in dbms
discuss the various types of join operations in dbms
relational algebra join operations in dbms
various join operations in dbms
discuss any 4 types of join operations in dbms
explain different join operations in dbms
explain join operations in dbms
what is join operations in dbms
join operations in dbms with example








Post Comment